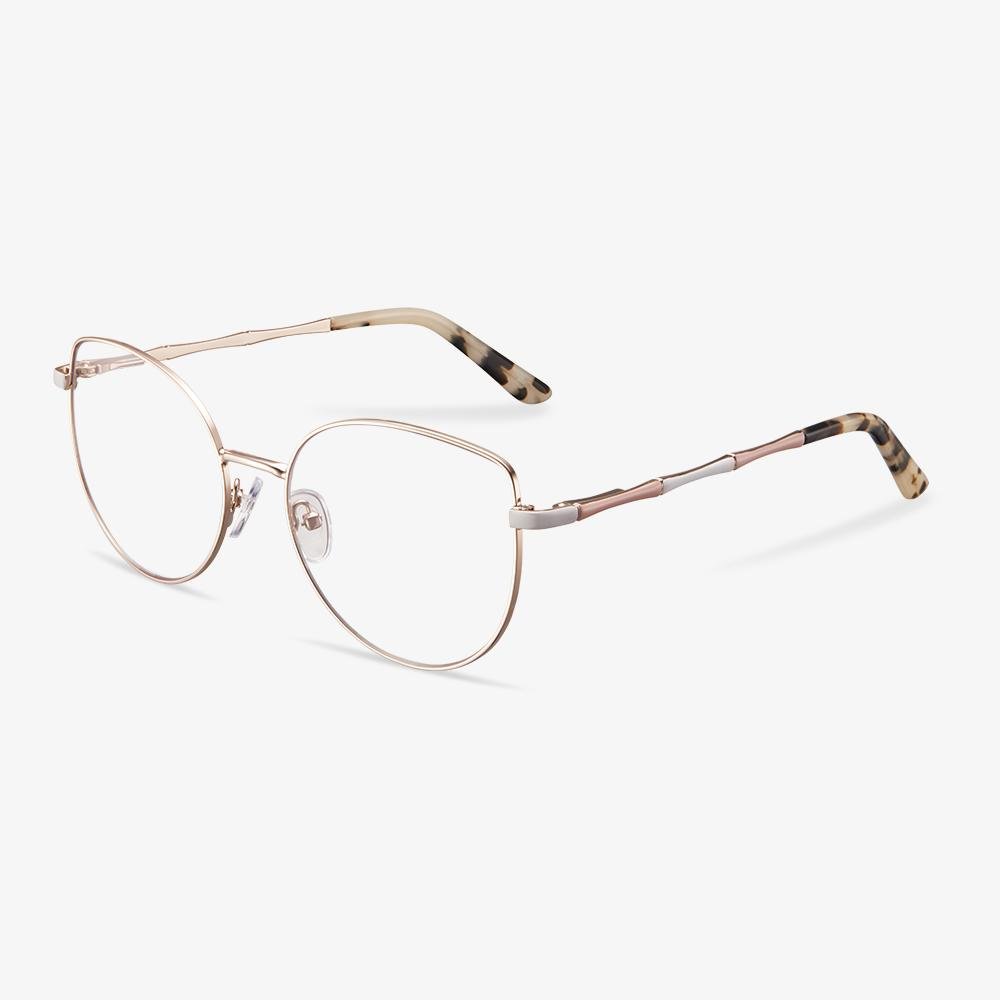
How many degrees of myopia do I need to wear glasses?
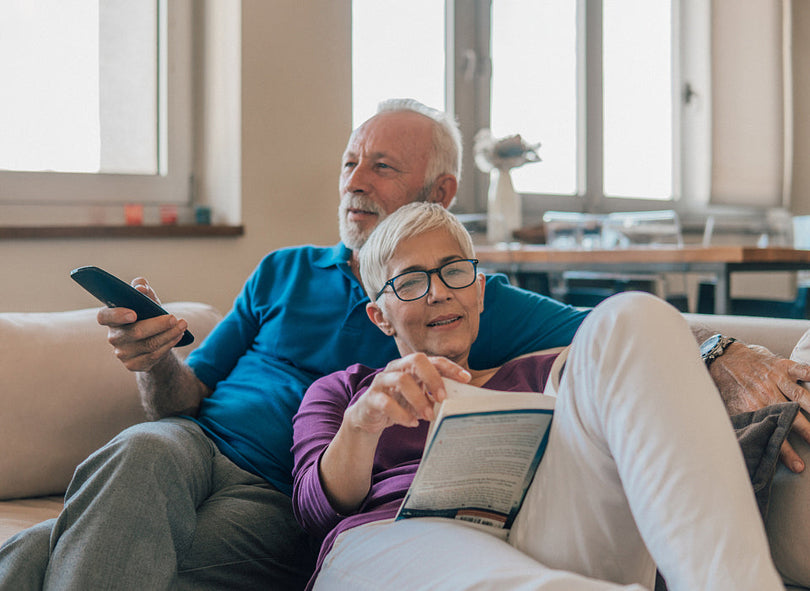
Students are the most nearsighted because they need to read and study every day. Many people have myopia during their student days. During the physical examination, everyone will check their eyesight first. Generally speaking, if the visual acuity is lower than 0.6, it means that you may be near-sighted to 0 degrees. At this time, you need to go for optometry to see the specific vision situation and see if you need to wear glasses. If the visual acuity tested exceeds 200 degrees, you must wear glasses at this time. If you do not wear glasses, your vision will be greatly affected, and the degree of myopia will rise quickly. For this reason, you must wear glasses in time to correct your vision. If the degree of myopia does not exceed 0 degrees, this is pseudo-myopia and does not require glasses. However, you should always take care to protect your eyes, avoid staring at things at close range for a long time, and don't let your eyes get too tired, so your vision will slowly return to normal.
How to maintain a hard-coated lens?
The hard-coated resin lenses can be identified by the sound of the tabletop tapping and the color brightness of the lenses. The lenses, which sound clear and have bright edges, are hardened. In daily use, avoid overheating environment. Avoid contacting with alkaline liquid, so as not to cause damage to the lens. And this damage is usually not formed in an instant.
Long-term use, sun exposure, and so on may make the coating slowly fall off. If the production of hard film technology is worse, the film is easier to fall off. When cleaning and adding a hard-coated lens, clean the particles on the front and rear surfaces of the lens with clean water first, and then blot dry with a clean soft cloth. Do not wipe the surface when the lens is dry.
The Advantages of Polycarbonate Glasses
In fact, polycarbonate glasses come with several benefits and this section will show some of them.
First, polycarbonate glasses are safe and are virtually unbreakable. A study found that polycarbonate glasses were more impact-resistance than glasses or other types of plastic lenses.
Second, polycarbonate glasses are thinner than other types of lenses. This feature makes them ideal for people who have strong prescriptions. Lighter and thinner eyeglasses are less likely to slip off your nose and are more comfortable for everyday wear.
Third, extended exposure to UV radiation from the sun can cause damage to your eyes and lead to some eye conditions such as cataracts or macular degeneration. Of course, polycarbonate glasses can block out harmful UV rays from the sun and provide good protection for your eyes.
However, there are some negative voices of polycarbonate lenses.
Who should wear blue light glasses?
Teenagers, middle-aged and old people need to wear blue light glasses. The lens of a teenager is clear, pure, and still developing. Their eyes are less resistant to blue light than adults and are more vulnerable to long-term exposure to blue light, which can promote the development of myopia. Teenagers study more nervous, are free to love to play computer games, love to watch TV programs. Blue light damage can be said to be everywhere. As a result, teenagers are among the biggest victims of blue light. Macular degeneration is a common disease in the elderly, usually occurring after the age of 45, and the incidence increases with age. Blue light can accelerate the progression of macular degeneration, especially in patients following cataract surgery. Blue-blocking glasses are still the best preventative measure.
Do blue light glasses actually block blue light?
Anti-blue light glasses are still popular on the market. This kind of glasses is said to be 'anti-radiation and anti-blue light', but this kind of hot-selling anti-blue glasses has many problems. At present, such anti-blue glasses mainly block or absorb blue light through special materials, but there are two misunderstandings in its blue light protection. One is that the protection is not preventable, and the other is that the color cast caused by the wrong protection makes visual fatigue aggravated. Studies have shown that our eyes are the most intolerant of blue light in the 400nm to 440nm band. Therefore, current manufacturers mainly block blue light in this band when producing anti-blue glasses. But the electronic products that we often come into contact with nowadays produce blue light between 450 nanometers and 490 nanometers, and anti-blue glasses have almost no protection in this wavelength. Generally speaking, the blocking rate of anti-blue glasses is 20% to 30%, but now the blocking rate of anti-blue glasses on the market basically reaches 80% to 90%. This high blocking rate can also easily cause a color shift. , It is easier to make the eyes tired.
Eye problems that may occur while driving.
Visual fatigue and xerophthalmia: when driving, the spirit and eyes are in a highly tense state, reducing the blink of an eye, which will easily cause eye fatigue and xerophthalmia. Flash glare -- car headlights and city light pollution -- can cause serious damage to the eyes. UV damage: UV radiation is strong when driving in the daytime, especially in the plateau and snow weather. Nocturnal myopia: nocturnal light is insufficient, so it can make the eye pupil dilate, causing nocturnal vision to drop influence driving safety.
What is a photochromic lens?
Photochromic lenses are lenses that become dark when exposed to a particular wavelength of light (usually ultraviolet light), but return to their original transmittance and become clear when no longer illuminated by the light source. Photochromic lenses can be made of glass or resin. The discoloration effect is caused by silver chloride or other halides added to the lens, which are transparent to visible light when not irradiated by ultraviolet light. When irradiated by ultraviolet light, chemical reactions will occur, which will absorb part of the visible light and make the lens show dark. The chemical reaction is reversible, so the lens returns to its original transparent state when it is no longer exposed to UV light.